Article
Coherent light scattering from cellular dynamics in living tissues
Reports on Progress in Physics
(2024)
Abstract
This review examines the biological physics of intracellular transport probed by the coherent
optics of dynamic light scattering from optically thick living tissues. Cells and their constituents
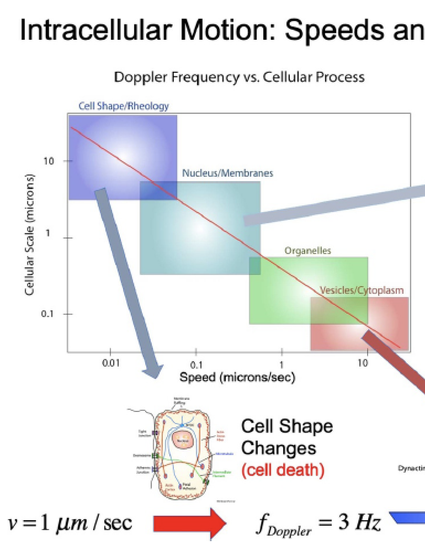
are in constant motion, composed of a broad range of speeds spanning many orders of
magnitude that reflect the wide array of functions and mechanisms that maintain cellular health.
From the organelle scale of tens of nanometers and upward in size, the motion inside living
tissue is actively driven rather than thermal, propelled by the hydrolysis of bioenergetic
molecules and the forces of molecular motors. Active transport can mimic the random walks of
thermal Brownian motion, but mean-squared displacements are far from thermal equilibrium
and can display anomalous diffusion through Lévy or fractional Brownian walks. Despite the
average isotropic three-dimensional environment of cells and tissues, active cellular or
intracellular transport of single light-scattering objects is often pseudo-one-dimensional, for
instance as organelle displacement persists along cytoskeletal tracks or as membranes displace
along the normal to cell surfaces, albeit isotropically oriented in three dimensions. Coherent
light scattering is a natural tool to characterize such tissue dynamics because persistent directed
transport induces Doppler shifts in the scattered light. The many frequency-shifted partial waves
from the complex and dynamic media interfere to produce dynamic speckle that reveals
tissue-scale processes through speckle contrast imaging and fluctuation spectroscopy.
Low-coherence interferometry, dynamic contrast optical coherence tomography, diffusing-wave
spectroscopy, diffuse-correlation spectroscopy, differential dynamic microscopy and digital
holography offer coherent detection methods that shed light on intracellular processes. In
health-care applications, altered states of cellular health and disease display altered cellular
motions that imprint on the statistical fluctuations of the scattered light. For instance, the
efficacy of medical therapeutics can be monitored by measuring the changes they induce in the
Doppler spectra of living ex vivo cancer biopsies.
Keywords
- dynamic light scattering,
- digital holography,
- optical coherence tomography,
- intracellular transport
Disciplines
Publication Date
March, 2024
DOI
10.1088/1361-6633/ad2229
Publisher Statement
Original content from this work may be used under the terms
of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence. Any further
distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the
title of the work, journal citation and DOI.
Citation Information
David D Nolte. "Coherent light scattering from cellular dynamics in living tissues" Reports on Progress in Physics Vol. 87 Iss. 3 (2024) p. 036601 ISSN: 1361-6633 Available at: http://works.bepress.com/ddnolte/59/
Creative Commons license

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons CC_BY International License.
